miniMD/LAMMPSのMPI周りを読んだ
miniMDというLAMMPSの開発チームが作っている軽量(.hと.cpp合わせて6500行程度)なMDコードを眺めた。
まずminiMD/LAMMPSのMPI並列のデザインをまとめてから、miniMD中の該当するコードを参照していく。
Parallel algorithm in miniMD/LAMMPS
Spatial decomposition
https://docs.lammps.org/latest/Developer_parallel.html#parallel-algorithms
LAMMPSではspatial decomposition に基づいてMPI分散する。simulation box を空間的に分割して、それぞれのsub-domainを各プロセスが担当する。
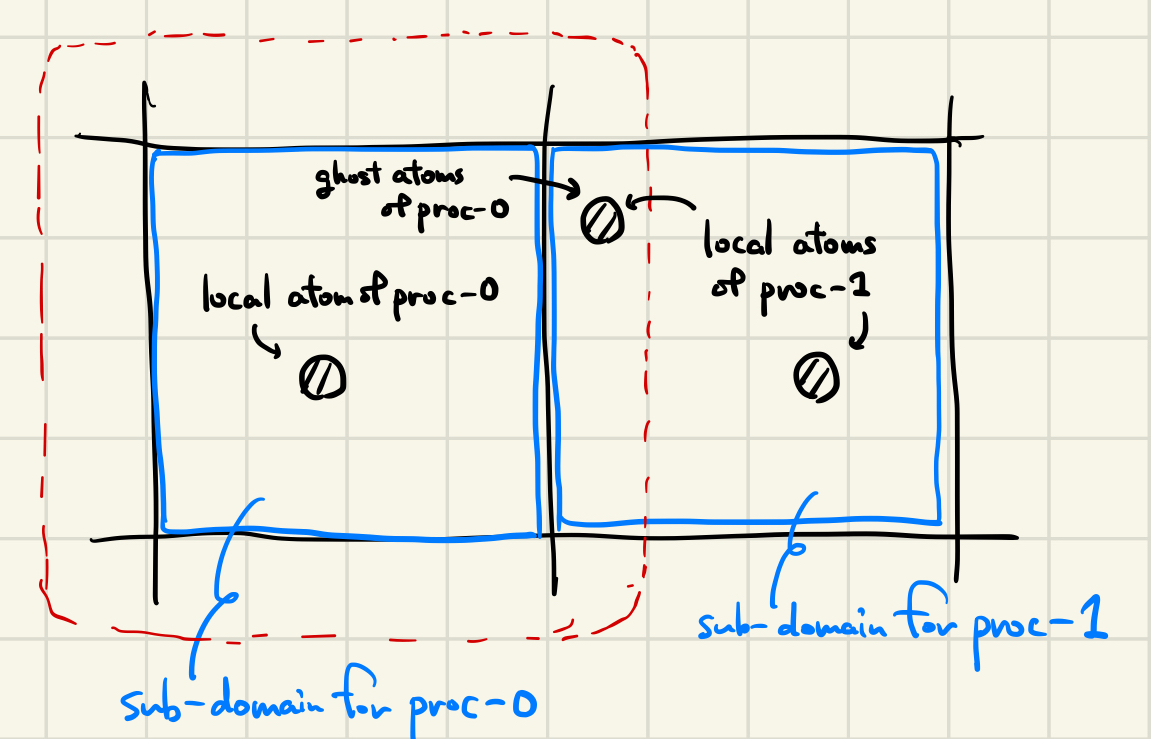
そのプロセスの担当するsub-domain にいる原子をlocal atom と呼ぶ(LAMMPSのドキュメントではowned atom と呼んでいるがコード内ではlocal atom と呼ばれている)。 ただし、各プロセスはlocal atom だけを保持しているのではなく、sub-domain の端からポテンシャルのカットオフ半径(から少し伸ばした距離)だけ広げた範囲に含まれる原子の情報も保持している。 この追加分の範囲に含まれる原子(隣のsub-domain を担当するプロセスにとってのlocal atom)はghost atom と呼ばれる。 上図では赤枠部分がプロセス0の追加分の範囲で、真ん中の原子はプロセス1にとってlocal atom として、プロセス0にとってはghost atom として、両方のプロセスが情報を保持する。
Communication pattern
https://docs.lammps.org/latest/Developer_comm_ops.html#communication-patterns
タイムステップごとに原子位置は変化するのでプロセス間で原子位置をMPI通信する必要がある。 これはforward communication と呼ばれている。
また、ghost atom に対して計算した情報をその原子を担当しているプロセスに送りたいことがある。 これはreverse communication と呼ばれている。 例えば、ghost atom jからlocal atom iへのpair force fijを計算したときに、fji は符号を反転するだけで得られるのでghost atom j にfjiを覚えさせて通信すれば演算回数を減らせる。
その他、neighbor list を更新するときにする処理はexchange とかborderと呼ばれている。
miniMD code reading
Integration
https://docs.lammps.org/latest/Developer_flow.html#how-a-timestep-works
miniMD/integrate.cpp at ab40f4c8b0808959abe1e60508e698d6d0d65ac1 · Mantevo/miniMD · GitHub
integrate.cppに各ステップごとにやることが書いている(LAMMPSのverlet.cppに対応)。とりあえずここから読み始めるとよい。
以下は擬コード
for(n = 0; n < ntimes; n++) { initialIntegrate(); if((n + 1) % neighbor.every) { comm.communicate(atom); // Forward communication of atom positions } else { // Rebuild neighbor lists comm.exchange(atom); // Send atoms outside box to a proper process comm.borders(atom); neighbor.build(atom); } force->compute(atom, neighbor, comm, comm.me); // Calculate forces if(neighbor.halfneigh && neighbor.ghost_newton) { comm.reverse_communicate(atom); // Send pair forces between local and ghost } finalIntegrate(); if(thermo.nstat) { thermo.compute(n + 1, atom, neighbor, force, timer, comm); } }
Communication in miniMD
Forward communication
送るlocal atom の原子位置をdouble配列に詰めてMPI_Sendrecvで送り合っている。
miniMD/atom.cpp at ab40f4c8b0808959abe1e60508e698d6d0d65ac1 · Mantevo/miniMD · GitHub
miniMD/comm.cpp at ab40f4c8b0808959abe1e60508e698d6d0d65ac1 · Mantevo/miniMD · GitHub
Reverse communication
同様に送るghost atom のforce をdouble配列に詰めてMPI_Sendrecvで送り合っている。
miniMD/atom.cpp at ab40f4c8b0808959abe1e60508e698d6d0d65ac1 · Mantevo/miniMD · GitHub
miniMD/comm.cpp at ab40f4c8b0808959abe1e60508e698d6d0d65ac1 · Mantevo/miniMD · GitHub
Neighbor list and newton pair
https://docs.lammps.org/latest/Developer_par_neigh.html#neighbor-lists
neighbor list に含まれる原子はneighbor flag とnewton flag によって決まる。
Half neighbor list (neighbor=half) with newton=off
miniMD/force_lj.cpp at ab40f4c8b0808959abe1e60508e698d6d0d65ac1 · Mantevo/miniMD · GitHub
あるプロセスのlocal atom i からみてカットオフ半径内に原子jがいるとき
- j がlocal atom ならば、(i, j)の組は原子iのneighbor list と原子jのneighbor list のどちらか一方にしか出てこない
- j がghost atom ならば、(i, j)の組は原子iのneighbor list と原子jのneighbor list の両方に含まれる(原子j のneighbor list は原子jがlocal atom であるプロセスが保持している)
以下はpotential energyとforce を計算する擬コード。 ポテンシャルを実装するときは、やってくるneighbor list に合わせて実装を書く必要がある。
for i in local atoms of process-p: fi = 0 for j in half neighbor list of atom-i: Compute fij (forces from atom-j to atom-i) fi += fij if j is local atom of process-p: f[j] -= fij Compute eij if j is local atom of process-p: eng_vdwl += eij else: eng_vdwl += eij / 2
Half neighbor list (neighbor=half) with newton=on
miniMD/force_lj.cpp at ab40f4c8b0808959abe1e60508e698d6d0d65ac1 · Mantevo/miniMD · GitHub
あるプロセスのlocal atom i からみてカットオフ半径内に原子jがいるとき
ghost atom jに足されたforce はreverse communication で対応するプロセスに送られる。 逆に、newton=onにしないとreverse communication が呼ばれない。 LAMMPSでも同様。
for i in local atoms of process-p: fi = 0 for j in half neighbor list of atom-i: Compute fij (forces from atom-j to atom-i) fi += fij f[j] -= fij Compute eij eng_vdwl += eij
Full neighbor list (neighbor=full)
miniMD/force_lj.cpp at ab40f4c8b0808959abe1e60508e698d6d0d65ac1 · Mantevo/miniMD · GitHub
あるプロセスのlocal atom i からみてカットオフ半径内に原子jがいるとき
意味的にはneighbor=fullならnewton=off(反作用の計算はしない)だが、ポテンシャルの計算をする部分でnewton flag は必要ない。
ただし、機械学習ポテンシャルを含むmany-body potential の場合、原子iのforceを計算するためにはカットオフ半径中の原子jのfull neighbor list が必要になることがある。 この場合、reverse communication で原子iのforceの一部を送る必要があるので、newton=onに設定しなければいけない1。
for i in local atoms of process-p: fi = 0 for j in full neighbor list of atom-i: Compute fij (forces from atom-j to atom-i) fi += fij Compute eij eng_vdwl += eij f[i] += fi
-
”half neighbor list の中身を決めるフラグ”と”reverse communicationを実行するかのフラグ”が使いまわされている。↩